Lightning Network as a Solution for Resolving Bitcoin’s Scalability Problem
Introduction
Why Are Blockchains slow?

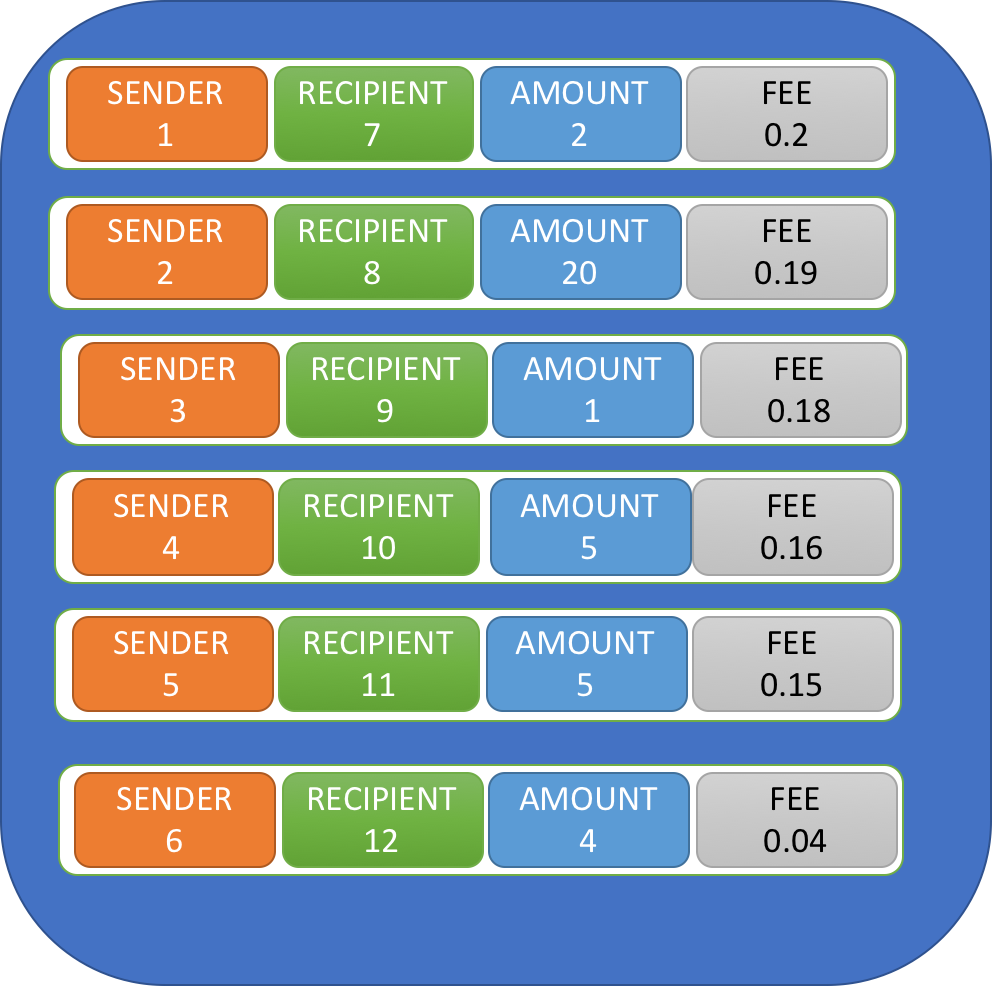
What is transaction fee?
So what is Lightning Network again?
Example:
And what are those payment channels?
Example:
How does network actually work?
Conclusions
The technology looks promising, but as always has a bunch of open problems need to be resolved.
For some cryptocurrency purists, this increased centralisation is reason enough to be against implementation of the Lightning Network. Most people who feel this way are in favour of larger blocks to scale the network, which has its own drawbacks as mentioned earlier.
Ultimately, these large payment hubs are not at all like central banks. They never actually possess or store your money in any way – that is still done by trustless smart contracts. Instead, they are simply a trustless medium for quick and cheap transactions.
From the other side LN has a couple of serious concerns regarding engineering:
Protocol decisions are still undergoing and require to have enough extensibility.
- Routing of micropayments might be an issue between different payment channels.
- The protocol must be as trustless as possible and verified prior production use.
- LN Reputation systems are centralising the network.
- Still opened a question about adding additional nodes.
- Traffic analysis is also an issue: micropayments are potentially even more sensitive than large transactions for tracking